Network Configuration¶
Now it’s time to set up the network for your virtual machine.
Android Settings¶
Before configuring the underlying networking of the virtual machine, you may wish to tweak some settings inside Linux.
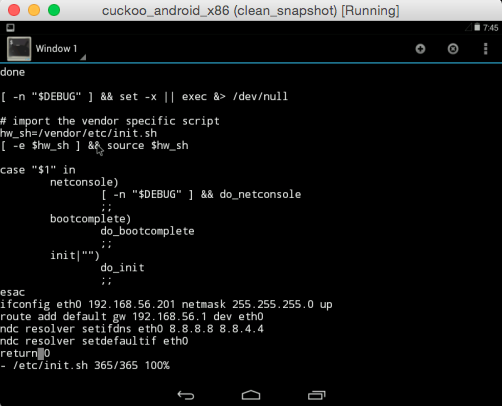
Open the Terminal app inside the machine and change to su. In
the file /etc/init.sh, edit eth0 settings.
For example, in the virtualbox network:
$ su
$ vi /etc/init.sh
#add inside the file
ifconfig eth0 192.168.56.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 up
route add default gw 192.168.56.1 dev eth0
ndc resolver setifdns eth0 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4
ndc resolver setdefaultif eth0
$ reboot
Android x86 on Virtualbox:
Virtual Networking¶
You need to decide how to make your virtual machine access the Internet or your local network.
In previous releases, Cuckoo used shared folders to exchange data between the host and guests. From release 0.4 on, it uses a custom agent that communicates over the network with a simple XMLRPC protocol.
To make it work properly, configure your machine’s network to allow the host and the guest to communicate. To make sue the virtual netsork was set up properly, test the network access by pinging a guest. Use only static IP addresses for your guest, as Cuckoo no longer supports DHCP. Using it will break your setup.
This stage depends heavily on your requirements and the characteristics of your virtualization software.
Warning
Virtual networking errors! Connectivity between host and guest must be ensured, as virtual networking is a vital component for Cuckoo. sure to get connectivity between host and guest. Most of the issues reported by users are related to an incorrect networking setup. If you aren’t sure, check your virtualization software documentation and test connectivity with ping and telnet.
The recommended setup uses a host-only networking layout with proper
forwarding and filtering configuration done with iptables on the host.
For example, using VirtualBox, you can enable Internet access to the virtual
machines using the following iptables rules (assuming that eth0 is your
outgoing interface, vboxnet0 is your virtual interface and 192.168.56.0/24 is
your subnet address):
iptables -A FORWARD -o eth0 -i vboxnet0 -s 192.168.56.0/24 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -j ACCEPT
iptables -A FORWARD -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
iptables -A POSTROUTING -t nat -j MASQUERADE
Add IP forwarding:
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1